Launching a new product can be risky, time-consuming, and costly. That’s why MVP development is a strategic approach adopted by successful businesses to validate product ideas early on. If you want to avoid building something no one wants, MVP development is your key to success.
At AssortTech, we offer Scalable Custom Software solutions with a focus on Custom Technology Integration. Our MVP design services help you build just enough to test, learn, and improve — without wasting time and budget.
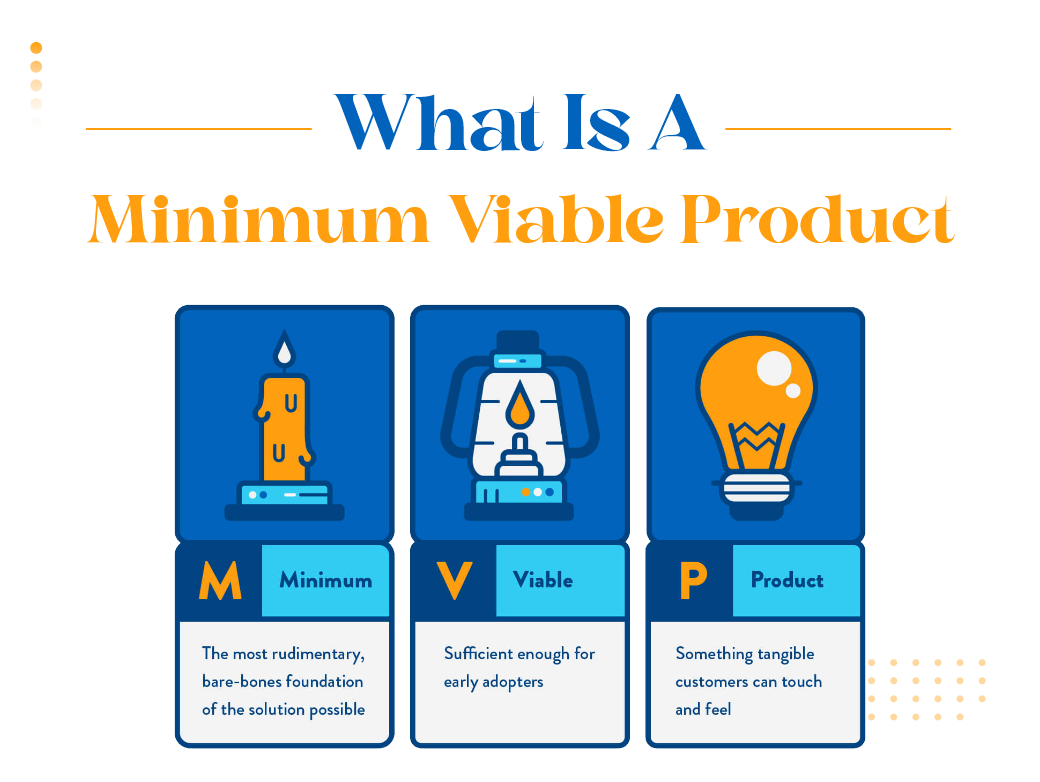
What is MVP Development?
MVP development refers to building a minimum viable product — a product version with the least but most essential features. It’s designed to attract early adopters and validate your product idea through real user feedback. The MVP acts as a bridge between concept and reality, helping development teams gather critical insights early on.
Under the lean startup methodology, validating a full-feature product upfront is risky and expensive. An MVP allows for experimentation and smarter decision-making at a lower cost.
Purpose of MVP Development
The core purpose of MVP development is to:
- Test your idea with real users before investing heavily.
- Launch a basic version of your product to the market quickly.
- Understand user preferences, needs, and pain points.
- Avoid resource waste on products that may not succeed.
With the right MVP design, companies gain clarity on product-market fit, saving time and resources for future development.
Requirements of MVP Development
Building a strong minimum viable product involves a few key requirements:
- Development Tools: Ensure access to necessary tech stacks and licenses.
- Deployment Platform: Choose platforms like AWS or Azure for reliable hosting.
- Manpower: Assign daily tasks to skilled professionals to maintain workflow.
Whether you’re launching a mobile app or SaaS platform, meeting these requirements helps execute your MVP efficiently.
Characteristics of an MVP
Two defining characteristics of effective MVP design include:
Minimum Features
A successful MVP contains only essential features needed to solve a user problem. For example, the first version of Snapchat let users send disappearing photos — simple, yet effective.
Viable and Functional
An MVP must deliver real value. It should function well enough that users want to engage with it. This ensures you receive meaningful feedback for future improvements.
Usefulness of MVP Development
MVP development supports:
- Early product idea validation
- Budget-friendly launches
- Rapid learning from user reactions
- Customer base building
- Informed product decisions
It also improves time-to-market, enhances agile workflows, and ensures your custom solution aligns with real market demand.
MVP Software Development Process
To develop a solid minimum viable product, follow this process:
Identify the Problem
Define a real problem your product will solve. This lays the foundation for a relevant MVP.
Study the Competition
Conduct market research to ensure your product stands out.
Prioritize Core Features
Focus on the must-haves that reflect your core value proposition.
Prototype the Solution
Use tools like Figma or AdobeXD to create an interactive prototype.
Develop the MVP
Choose a development method: no-code tools, in-house, or professional developers.
Collect Feedback and Iterate
Establish feedback loops using surveys and feature buttons to improve the MVP.
Critical Benefits

- Core Focus: Zero in on your product’s main value.
- Cost Efficiency: Avoid overspending on unnecessary features.
- Faster Market Entry: Launch quickly and start learning.
- Customer Feedback: Gain real insights from early users.
- Experimentation: Test assumptions and adapt fast.
- Strategic Growth: Use MVP learnings to plan the full product roadmap.
- Investor Attraction: Show proof-of-concept to attract funding.
At AssortTech, we guide businesses through every step of MVP development, ensuring your vision is executed strategically with scalable technology.
Drawbacks of MVP Development
While powerful, MVPs also come with challenges:
- Lack of Viability: Avoid building something too minimal that fails to attract users.
- Poor User Understanding: If users can’t grasp the product’s value, feedback becomes ineffective.
- Quality Trade-Offs: Don’t sacrifice usability for simplicity. Your MVP must still work smoothly.
Mitigating these risks requires careful planning and collaboration with an experienced development team.
Conclusion
MVP development is more than just a product strategy — it’s a mindset that supports lean, efficient, and smart innovation. With a clear focus, well-planned MVP design, and actionable feedback loops, you can create products that users love and businesses can scale. Pair this with the Discovery Phase: Purpose, Stages, Fundraising and Benefits, and you’ll create a comprehensive roadmap from ideation to execution.